Public Safety
Medical Rescue Team South Authority trains to bring the pinnacle of medical care to your doorstep. EMS is just small section in the continuum of emergency care. The first step in emergency care begins with you!
CPR
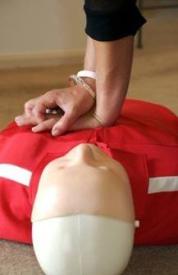 Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is the most important thing a bystander can do in the instance of cardiac arrest.
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is the most important thing a bystander can do in the instance of cardiac arrest.
While we encourage everyone of any age to attend CPR training, you can do CPR even if not certified. If someone isn’t breathing, call 911 and push hard and fast in the center of the chest.
- Every minute CPR isn’t performed the chance of survival decreases 10%
- Bystander CPR can double or triple chance of survival
- 475,000 Americans die every year from cardiac arrest
- 350,000 cardiac arrests occur outside the hospital every year
- 70% occur in homes and residences
- 18.8% occur in public settings
Learn more about CPR statistics.
FAQ’s
Q: If I do CPR without being certified can I get in trouble?
A: Pennsylvania Good Samaritan Law protects civilians who in good faith, attempt to render emergency care.
Q: Do I have to mouth to mouth?
A: The AHA no longer recommends mouth to mouth. Instead focus on chest compression.
Q: I’m afraid I may hurt the patient?
A: It is normal for chest compressions to result in some broken ribs, this should not discourage you from rendering aide. Broken bones are easier to fix then a heart.
Stop the Bleed
Trauma is one of the leading causes of death of young people. You can bleed out in as little as 5 minutes. Bleeding control is a simple and important lifesaving skill.
A STOP THE BLEED® course is for people who are interested in learning this lifesaving skill. The American College of Surgeons STOP THE BLEED® campaign has trained over 1 million people including students, teachers, and community groups. We are committed to training anyone who is old enough to understand what the course teaches and is interested in learning how to STOP THE BLEED® and save a life. Learn more
Sign up for a STOP THE BLEED® Certification Class.
Stroke

Stroke is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the U.S. Stroke can happen to anyone — any age, any time — and everyone needs to know the warning signs.
- On average, 1.9 million brain cells die every minute that a stroke goes untreated.
- Stroke is an EMERGENCY.
- Call 911 immediately.
Early treatment leads to higher survival rates and lower disability rates. Calling 911 lets first responders start treatment on someone experiencing stroke symptoms before arriving at the hospital.
FAQ’s
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of a warning stroke (mini stroke)?
A: A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a warning stroke, but is commonly referred to by the public as a mini-stroke.
TIA is a medical emergency with the same symptoms as ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. Because most TIA symptoms last from only a few minutes up to 24 hours, they are often dismissed and not taken seriously.
TIAs, which occur before about 15% of strokes, are considered "warning strokes" — they are associated with additional TIAs, full-blown strokes or other cardiovascular problems later. Most of these later health problems happen within just days or weeks of the TIA, so early interventions to reduce risk are vital.
Remember "B.E.F.A.S.T." to know when to call for help:
- B = Balance
- E = Eyes
- F = Face drooping
- A = Arm weakness
- S = Speech difficulty
- T = Time to call 911
If you or someone with you is experiencing these or other stroke symptoms, urgent medical evaluation and treatment are needed. Check the time so you'll know when the first symptoms appeared.
Call 911 even if the symptoms go away.
Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
Just as CPR is a key component of cardiac arrest, early defibrillation is also important. This can be done by bystanders like you. AED’s when turned on will walk you through how to place them and use them.
To increase the chance of survival of cardiac arrest. MRTSA advocates for the placement and accessibility of public AED’s in and around:
- Public areas
- Workplaces
- Businesses
We also recommend that anywhere an AED is placed, a Stop the Bleed kit is placed with it.
AED’s and Stop the Bleed kits can be pricy, but it only takes one use to change a life. Because of this investment, we recommend you contact us prior to buying anything. While MRTSA does not recommend or endorse a specific brand or product. Some products allow us to integrate the AED technology into our resuscitation when we arrive, with some transmitting data to our mobile computers. This allows us to better help the patients we serve.
Seat Belts
Motor vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death in the first three decades of American’s lives. In 2009 alone, crashes killed over 33,000 people and injured another 2.2 million—more than 70% of these were in passenger vehicles and trucks.
More than half of the people killed in car crashes were not restrained at the time of the crash. Wearing a seat belt is the most effective way to prevent death and serious injury in a crash.
- 1 in 7 people still don’t buckle up
- Most drivers and passengers killed in crashes are unrestrained. 53% of drivers and passengers killed in car crashes in 2009 were not wearing restraints.
- Seat belts dramatically reduce risk of death and serious injury. Among drivers and front-seat passengers, seat belts reduce the risk of death by 45%, and cut the risk of serious injury by 50%.
- Seat belts prevent drivers and passengers from being ejected during a crash. People not wearing a seat belt are 30 times more likely to be ejected from a vehicle during a crash. More than 3 out of 4 people who are ejected during a fatal crash die from their injuries.
- Seat belts save thousands of lives each year and increasing use would save thousands more. Seat belts saved almost 13,000 lives in 2009. If all drivers and passengers had worn seat belts that year, almost 4,000 more people would be alive today.
- In one year alone, crash deaths and injuries to drivers and passengers cost $70 billion in medical and lost work costs.
More than half of the people killed in car crashes were not restrained at the time of the crash. Wearing a seat belt is the most effective way to prevent death and serious injury.
